Liver Cancer: Symptoms, Risks, and Treatment Options
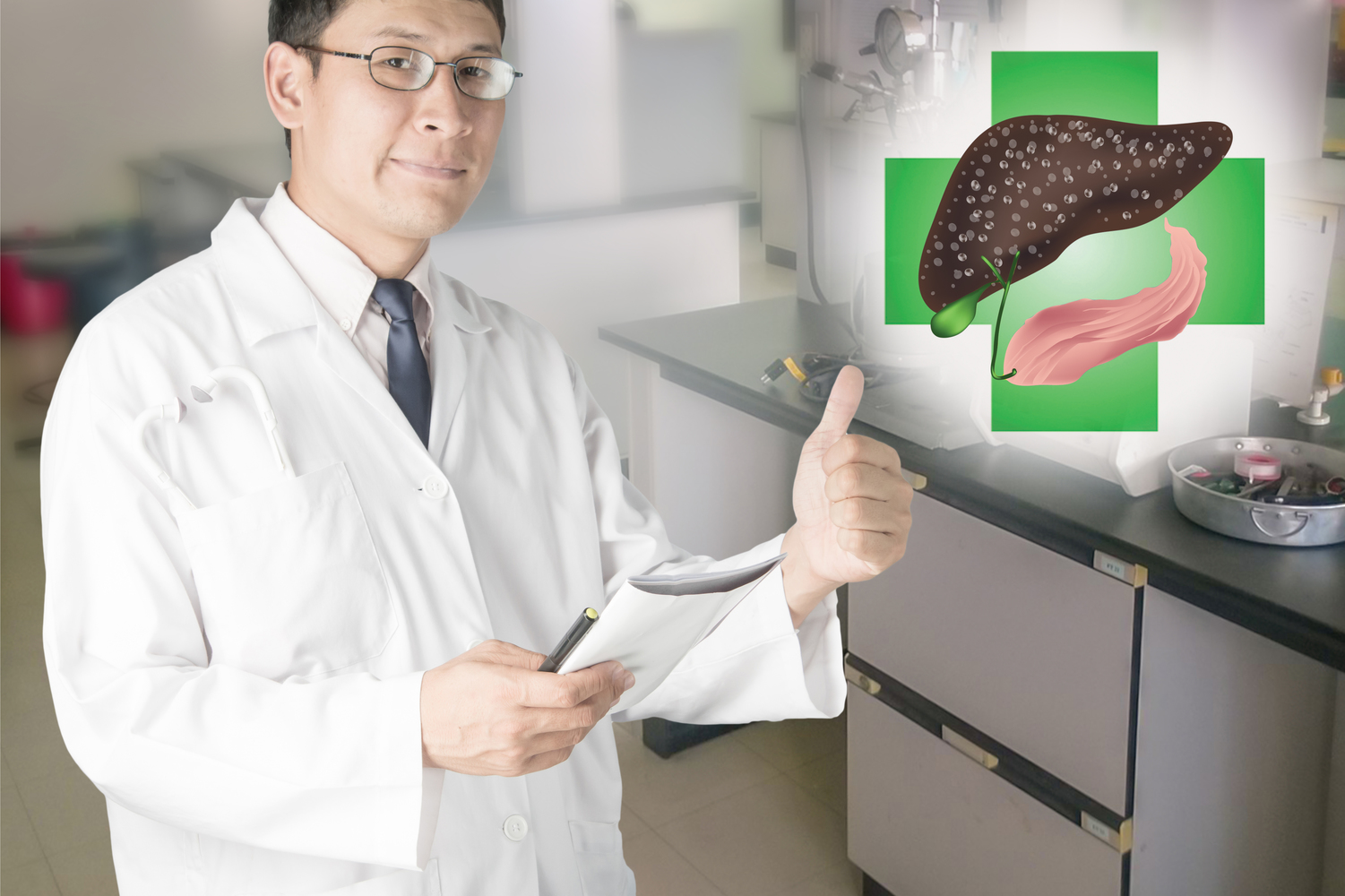
Liver cancer is the result of cancerous cells growing and spreading in and around the liver. The cancer that begins in the liver is referred to as primary liver cancer. For example, HCC or hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the primary liver cancers. Metastatic liver cancer spreads from organs outside the liver. Statistics show more than 30,000 people in the US diagnosed with this cancer every year. It is more common in men than women.
Here are some must-know facts about liver cancer:
1. Causes of liver cancer
Like with any other cancer type, some people are more likely to have liver cancer than others. Some of the common risks and contributing factors include, but are not limited to:
- Excessive use of alcohol and tobacco
- Exposure to or having Hepatitis B and C infection. This disease is linked to liver cancer as a result of cirrhosis, a chronic liver disease that causes inflammation and degeneration of normal liver cells.
- Obesity, diabetes. fatty liver disease are a few other causes of liver cancer. Here the liver abnormality takes place which may increase the probability of cancer. Coupled with other infections it may lead to liver cancer.
- Exposure to aflatoxins, a type of fungi that are found in certain crops such as maze, almonds, cotton seeds and tree nuts
- Liver diseases and autoimmune diseases may also cause liver cancer. Some rare illnesses such as Wilson disease and Tyrosinemia can result in cirrhosis which, like mentioned above, increases the probability of liver cancer
2. Symptoms of liver cancer
There are certain symptoms that are common to other illnesses and unique to liver cancer. For instance:
- A person with liver cancer may feel tired, bloated and experience pain in the upper back, shoulder or abdomen, generally on the right side of the body.
- The patient may have nausea, weight loss, weakness, jaundice, fever, loss of appetite or feeling of fullness
- Lump near the rib cage on the right side.
- Dark colored urine.
3. Diagnosis of liver cancer
The treating physician may conduct a physical examination to look for the possibility of the disease. This may be followed by blood tests, a CT scan, ultrasound scan, MRI, Angiogram – a combination of one or more of these tests. The physician may also perform a liver biopsy. Here, a small piece of tissue in the liver is removed and inspected under the microscope to confirm or rule out cancer.
4. Treatment for liver cancer
Many factors influence the treatment options of liver cancer patient. For instance, the age of the patient and his or her overall health condition is crucial in determining the treatment strategy. The size, number and location of the tumors are also important. If the cancer hasn’t spread to other parts of the body, the doctor may perform transplant or replacement of the liver. If some part of the liver is healthy, a surgery may be enough to cure.